As a Blender artist, I know how hard and complex it can be to bake textures in Blender. I'm sure you've been there too - stuck trying to figure out why your textures aren't working the way you want them to. Well, don't worry! In this article, we'll walk you through the steps of baking textures in Blender step-by-step so that you can finally get those perfect results!

What is Bake in 3D Modelling?
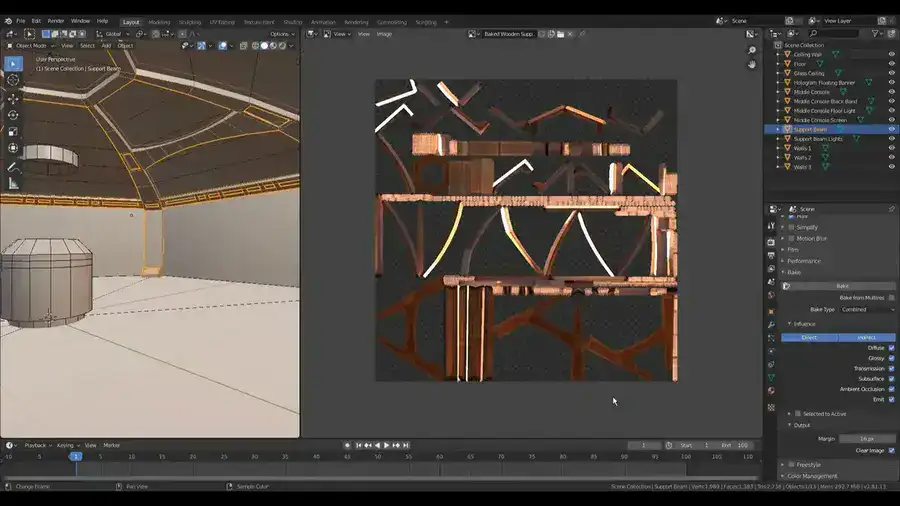
Baking is the technique of fusing a high-poly model with a low-poly one for computer processes like simulations and animations.
The use of textures in 3D modeling is one of the most widely used baking applications. This process allows 3D artists to texture their 3D models by combining multiple textures from their high-poly models into a single texture sheet (or map). This reduces the data smaller so that game engines, internet viewers, and social media platforms like SparkAR and Snapchat may use them with AR.
Also read: How to Measure in Blender
In order to better understand how baking actually functions, let's quickly go through its foundations. A high-poly (containing many polygons) and a low-poly (consisting of fewer polygons) model must be created before any baking technique can begin (made up fewer polygons). The high-poly model should be accurate enough to capture all the characteristics necessary for texturing, while the low-poly model should have enough information to support future animations and simulations.
Your high-poly original model will be converted into an optimized version with all of its detail on a noticeably reduced mesh, making it perfect for use in game engines or online viewers. These basic steps ought to give you an idea of what goes into ensuring that our 3D models always look fantastic regardless of where they are used, although there are undoubtedly many more complicated techniques when it comes to baking.
How to bake textures in Blender Eevee?
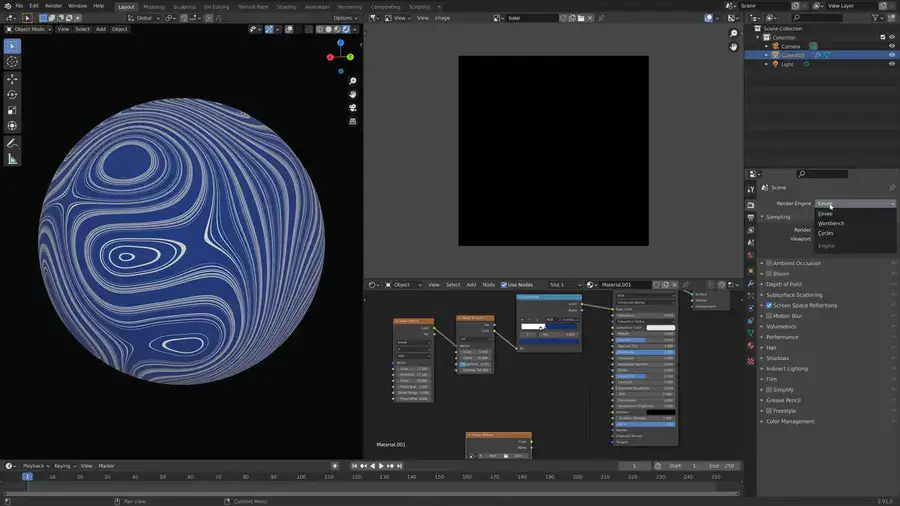
Baking textures in Blender Eevee & Cycles is simple, but it's vital to understand the overall process.
Baking PBR texture sets requires diffuse, roughness, normal map, and metalness. Depending on your workflow, shader masks can be generated during baking.
You'll usually start by creating a simple PBR texture map in Blender Eevee. This includes developing the essential fundamental textures (diffuse color and roughness) and any procedural texturing for your product or project. The Extreme PBR Evo add-on is ideal for fast creating these textures because it lets you build a variety of materials with a few clicks.
After procedural adjustments, UV map and bake final textures. Select all modular asset elements that need a non-overlapping UV Map and proceed to Object Data Properties (the green triangle icon on the left side panel). In this properties panel, enter the UV Map section and click the '+' sign to create a new UV Map slot for each selected piece of geometry.
Now assign each object or group of objects in your scene to an existing UV Map slot or create new slots if needed with the plus sign icon (hint: make sure they're non-overlapping so no two components share the same area on one image). After assigning everything, we may run the baker. Crouching in our viewport window, switch from Cycles Render engine to Eevee Render engine, then press Alt + B to bring up our Bake pop-up menu options (normals/diffuse/roughness etc.). Ready? Click bake! Blender's Image Space should now display our baked PBR textures.
Does Blender use GPU for baking?
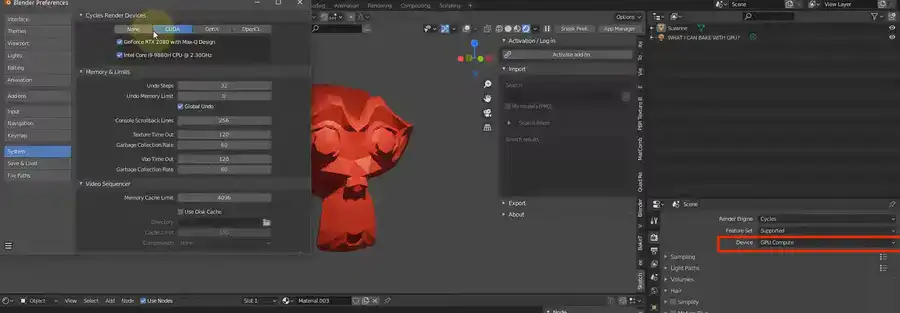
The short answer to this question is a resounding yes! Blender baking can be enabled with a few clicks. To render, click Render on the top toolbar. On the properties panel's left side, click Render. In this part, you can choose CPU or GPU in the Device area. If you have an NVIDIA graphics card, pick GPU and click bake.
Related: How to Repair a Mesh in Blender
GPU baking allows artists like me to quickly produce baked maps without overloading CPUs or waiting long between bakes. It reduces noise when generating lightmap textures, which helps with complex scenes and lighting.
Is baking necessary in Blender?
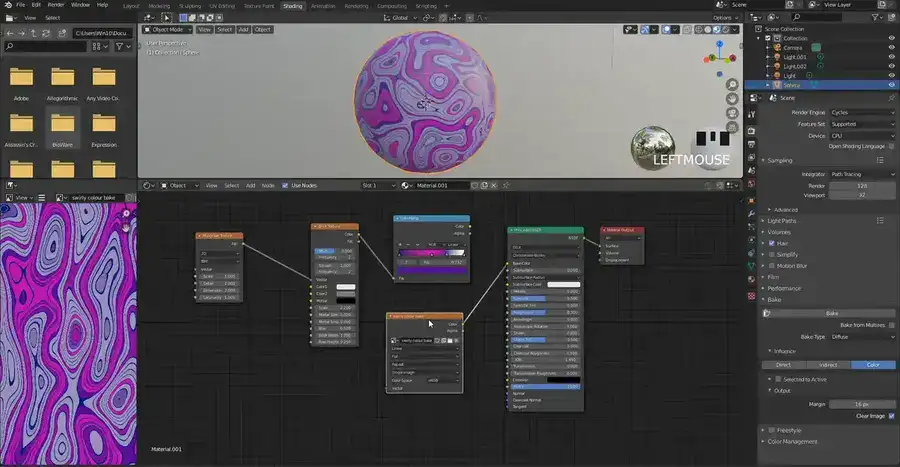
Baking models creates textures and normal maps. Textures add color and detail to a model. Normal maps provide a low-resolution model high-resolution details. If you intend to achieve any of these, then you should be baking your textures.