As an avid Photoshop user, you will agree that selecting specific objects in a photo can be challenging. Thanks to the Quick Selection tool, this can be done easily and quickly. The Quick Selection tool is one of the many ways to select parts of a photo in Photoshop.

This tool uses colors to manually identify the section you want to select and is the perfect option for images with many different colors and contrasts. In this article, we’ll guide you through how to use this tool properly, as well as tips and tricks for a seamless selection in Photoshop.
Where is the quick selection tool?
First off, before we delve into the how-to section of this article, let’s clarify where the Quick Selection tool is located in Photoshop.
To access the Quick Selection tool, head over to the toolbar located on the left side of the screen. It is the fourth option from the top.
How to use the quick selection tool?
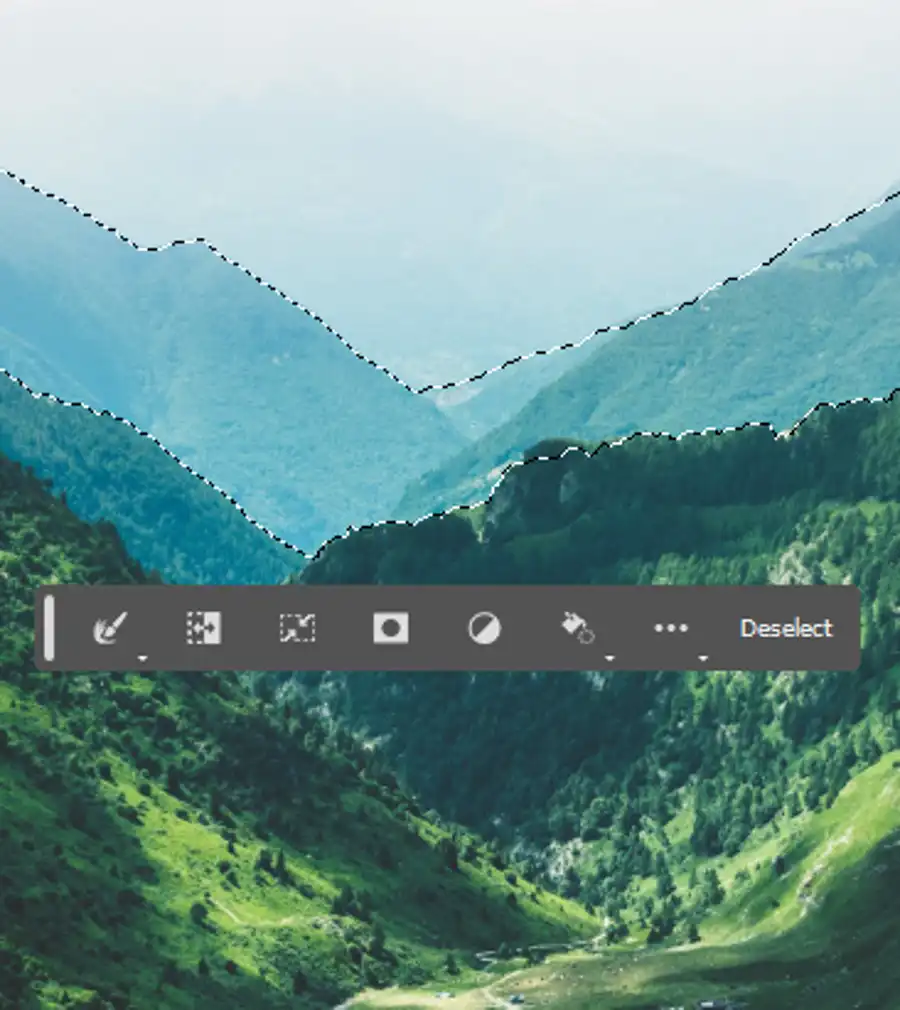
The Quick Selection tool can be used to select parts of an image that have different colors and brightnesses.
- To begin using the tool, start by dragging over an area you want to select. The tool automatically expands the selection in a way that includes similar colors until it reaches edges that are different from the initial selection. This is useful when selecting complex shapes with multiple colors.
- To add to the initial selection, drag over another area you want to include. To subtract from the initial selection, press the Option or Alt key while dragging over an area. This will remove the specific area or object from the selection. It's important to note that the size of the selection brush has to be smaller than the region or object you’re trying to select.
When making a selection, it's best to customize the tool's size for more accuracy. This can be done by changing the size of the brush from the top toolbar. This toolbar also contains other options such as refining the selection, changing the brush hardness, and feathering.
It's also good practice to use the Quick Selection tool with layers. Layers in Photoshop enable you to sort what's on top of what, and this tool can be best used with layers. Copying the current layers is an excellent way to protect your work, preserve an unedited version of the image, and blend two versions of an image if desired.
How to undo quick selection?
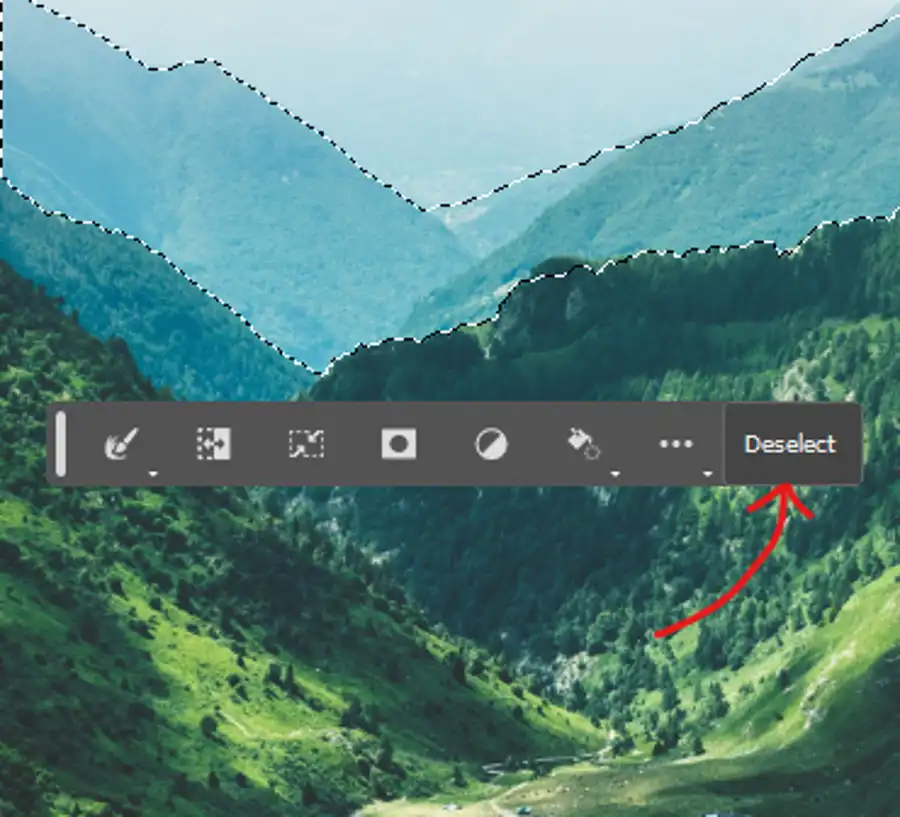
If you make a wrong selection, you can right-click and select "Deselect" to remove the selection. After making a selection, you can right-click the selected section for additional options such as "Select Inverse." This is useful when you want to select the opposite of what you have just selected.
Questions you might be asking
How do I cut with quick selection tool?
To cut with the quick selection tool in Photoshop, first select the quick selection tool from the toolbar. Then, use the tool to click and drag over the area you want to select. If you need to add or subtract from your selection, use the brush tool to paint over the area. Once you have your selection, press Ctrl+X (Windows) or Cmd+X (Mac) to cut the selected area out of the image.
How do you use the quick selection tool accurately?
To use the quick selection tool accurately, start by zooming in on the area you want to select. Then, adjust the brush size to match the area you're selecting. Use short, controlled strokes and try to stay as close to the edge of the object as possible. If you accidentally select an area you don't want, press Alt (Windows) or Option (Mac) to switch to the subtract option and paint over that area. Keep refining your selection until you have accurately selected the entire object.
How do you use the object selection tool in Photoshop?
To use the object selection tool in Photoshop, select the object selection tool from the toolbar. Then, drag a box around the object you want to select. The tool will automatically select the object and create a selection border around it. If the selection is not accurate, you can use the refine edge tool to fine-tune the selection. Once you have your selection, you can manipulate it by moving, copying, or deleting it from the image.

